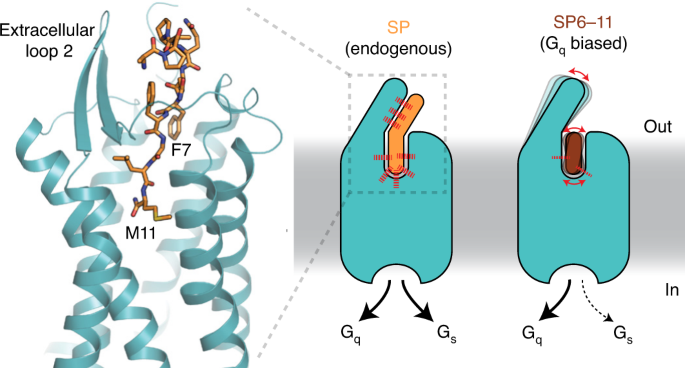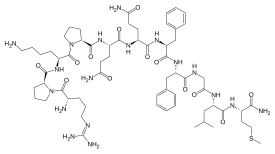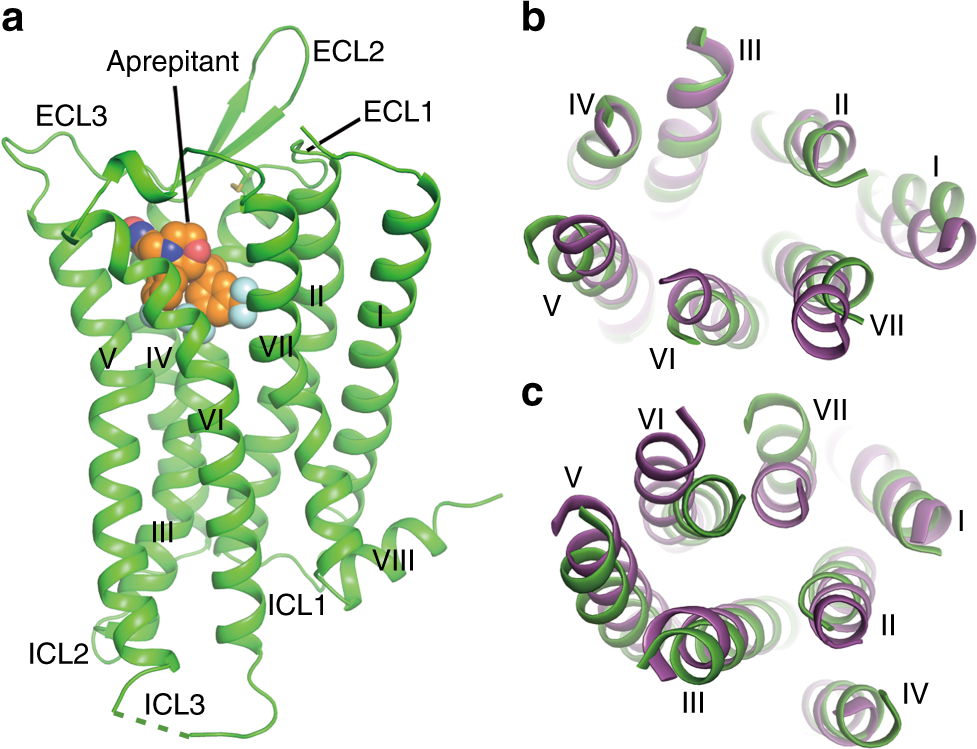
Human substance P receptor binding mode of the antagonist drug aprepitant by NMR and crystallography | Nature Communications
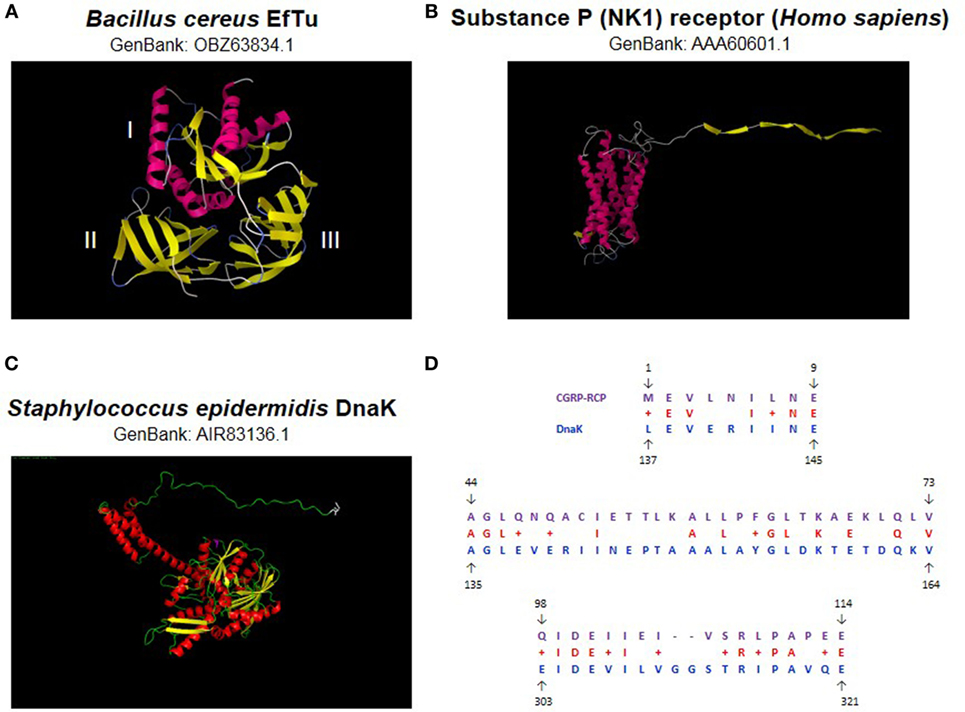
Frontiers | Substance P and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide: Key Regulators of Cutaneous Microbiota Homeostasis

MCN II L8 Wetzel Signalling- Amino acid sequences of neuropeptides-fig 6.22 pg 138- 118 Diagram | Quizlet
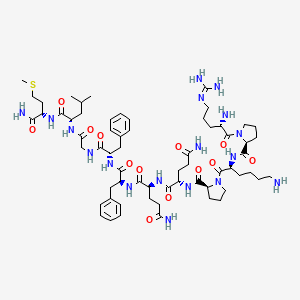
Structure of substance P (SP) peptide and its analogues used in this work. | Download Scientific Diagram

The role of substance P in inflammatory disease - O'Connor - 2004 - Journal of Cellular Physiology - Wiley Online Library

Table 1 from The Impact of Substance P (SP) N-Terminal Metabolite SP1-7 in Opioid Tolerance and Withdrawal | Semantic Scholar

The emerging role of substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor signaling pathways in growth and development of tumor cells | SpringerLink

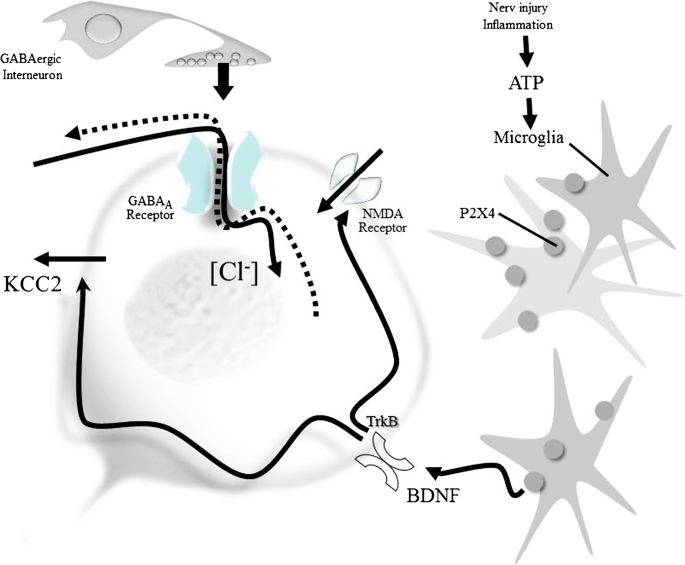
Frontiers | The Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Substance P/NK-1R Interactions in Inflammatory CNS Disorders

Structural analysis of the neuropeptide substance P by using vibrational spectroscopy | SpringerLink